A disaster could hardly be planned, but disaster recovery planning is a must. The core of successful disaster recovery is, of course, backup.
Nowadays, cloud storage providers are widely used for storing backups. However, the biggest cloud storage providers have created various services to perform recovery in the cloud. Today we will discuss the need for disaster recovery in the cloud and its peculiarities.
What is a Disaster and how to Recover?
A disaster in IT world is a situation when you are unable to perform business tasks. Disaster recovery, hence, is a process of restoring the ability to perform these tasks and operations. In the modern world, that operation should be done fast.
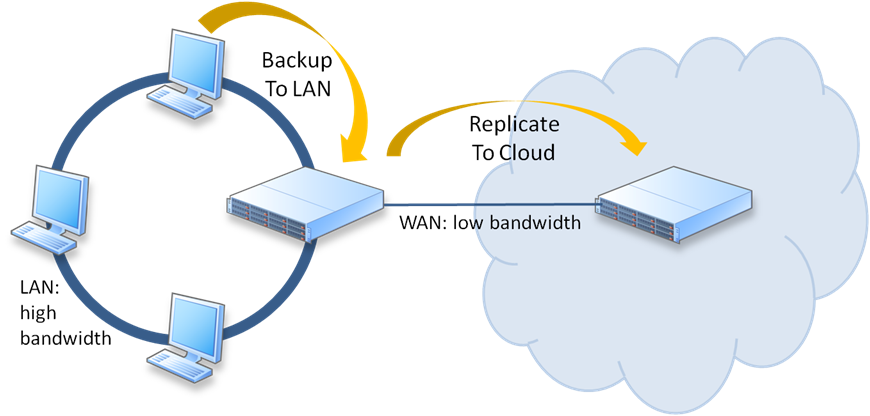
One of the best solutions is to keep data backed up on-site and in the cloud at the same time. This is called 3-2-1 backup strategy. When you need to restore anything – it is faster and cheaper to restore from the local backup. But when your local backup and half of your office is flooded with water or have burned to the ground – cloud backup could be the only way to restore operations.
The development of the modern cloud infrastructure allows you to not only restore data from the cloud to your local machines but to restore your whole IT-infrastructure in the cloud: users machines, Exchange and SQL servers, the lot. Recovery to the virtual environment is ideal if you wish to:
- Scale up and down to take into account the workflow and user demands
- Run as “pay-as-you-go”, when you pay only for the resources used
- Are optionally replicated among several data centers, consequently, tolerant to natural disasters, power cut-offs, and hardware failures
- Can be accessed both via the Internet and offline
- Support strong encryption and don’t take part in it, so only the owner can access the data

A cloud provider is responsible for virtual machine maintenance, and the administering routine is effortless. It is possible to deploy a custom build image within CloudBerry Backup (CBB) in a couple of clicks – check our Physical to Virtual Recovery Guide. Thanks to virtualization and location of resources in the same network, a virtual machine starts faster and the process is more convenient than it is with a physical one.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Each cloud has numerous OS and software VM bundles, which can be started in a second. However, corporate IT-infrastructures usually contain many custom configurations and solutions, so it’s almost utopian to recover them by only importing user settings and data. That is why CBB can create a full-featured image-level backup. But you still have to consider the strategy of backup delivery to the cloud. There are two main approaches:
- Local to Cloud (LtC) recovery is based on storing backups on the local facilities and transferring them to the cloud in case of disaster
- Cloud to Cloud (CtC) recovery uses backups, which are already stored in the cloud
Each scenario has its pros and cons, so it’s hard to evaluate them at once. We created a table for you to compare the advantages of both variants.
| Criterium | Local to Cloud | Cloud to Cloud |
| Durability | Low – data is stored onsite | High – data is stored offsite and replicated |
| Transfer speed | Depends on the network bandwidth, can be fee-based | High, usually free within one cloud provider |
| Backup size | Limited by physical restraints | Unlimited |
| Local IT-infrastructure necessity | Required | Not required |
| Expenses | Hardware & software cost, maintenance, energy charge, server room lease and conditioning, etc. | Charge for utilized resources* |
*Read our article about Amazon S3 Storage classes to find out how to save on cloud storage.
Honestly speaking, local backup storage rarely remains untouched, when the remaining IT-structure is affected by a disaster. Thus, data will be definitely lost, if it isn’t backed up somewhere offsite. Natural disasters and anthropogenic catastrophes rarely come when the business is ready, so having backups stored offsite is a good idea. Another concern is big data upload – it will take days to transfer over 10TB backup even through a fast network.
Meanwhile, a cloud VM can pick up block storage in the same availability zone without extra relocation.
There are also some complex restoration strategies, as well as uncommon approaches. We have a white paper on disaster recovery in the cloud, where you can learn more.
Best Cloud Storage Provider for Recovery
The last concern is choosing the cloud endpoint for recovery. There are a lot of cloud providers today, though only three of them have ripe solutions that are widely used in business. They are as follows:
- Amazon Web Services is a diversified system of cloud facilities. Alongside with storage and virtual machines, it offers database platforms, data transfer facilities, cold and archive data repositories, etc. Amazon is one of the oldest players at the cloud services market, and it offers significant discounts for long-term subscriptions. Amazon is running it’s own virtual environment service, the EC2, which is scalable and cost-effective.
- Google Cloud Platform also offers various virtualization, storage, and big data processing tools, which were developed alongside with such services as Gmail and Google Docs. It allows creating virtual machines with custom resource configurations, thus helping to save on the recovery time.
- Microsoft Azure is another complex service, which has different infrastructures, platforms and software as a service. Besides native popular server bundles support, it offers fast cold storage, which is good for storing backups for disaster recovery.
It’s hard to select the platform that fulfills all business requirements, so we have compared these platforms for computing, analyzed the prices and looked through their backup features to facilitate your choice. Nevertheless, you don’t have to stick to the one and only provider. CloudBerry can deploy Amazon Elastic Compute 2 (EC2), Microsoft Azure virtual machine or Google Cloud VM from the server image stored on local or cloud storage, which opens great prospects for cloud migration with high accessibility and convenience.
Moreover, cloud storage can be combined. CloudBerry Cloud to Cloud backup feature helps moving data across different clouds, so you can create a custom backup lifecycle. The encryption and compression option can be changed on the way, so it’s possible to meet any storage requirements.
Conclusion
Now you can see that disaster recovery in the cloud is more flexible, cost-effective and faster than any physical restoration. Everything you need is planning and reliable tools. CloudBerry license is permanent and movable, with recovery activities free of charge. Work out your recovery strategy now with a full-featured free 15-days trial and do not hesitate to ask any questions in the comments section below.
